Internal medicine includes cardiology. A cardiologist and a cardiac surgeon are not the same thing. A cardiac surgeon performs heart surgery by opening the chest. When dealing with a complex health condition such as heart disease, it is critical to find the right fit between us and our specialist. A diagnosis of heart or vascular disease is frequently initiated by the primary care physician, who then refers patients to a cardiologist. The cardiologist examines the symptoms and medical history and may suggest tests to make a more definitive diagnosis.
Because cardiology is a complex field, many cardiologists specialise in various areas. Clinical cardiologists are all doctors who specialise in the diagnosis, medical management (the use of medications), and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Clinical cardiologists who specialise in paediatric cardiology diagnose and treat heart problems in children. Clinical cardiologists who only treat adult patients are known as adult cardiologists.
What is a cardiologist?
A cardiologist is a physician who specialises in heart and blood vessel diseases. They can treat heart disease and help you avoid developing heart disease. To become a cardiologist in the United States, one must first complete four years of medical school, three years of internal medicine training, and at least three years of cardiology training.
A cardiologist can take the American Board of Internal Medicine exam after completing ten years of training. Even after receiving board certification, cardiologists continue to learn as long as they practise. To provide the best care, they must stay current on the latest advances in patient treatment.
What exactly does a cardiologist do?
A cardiologist is a doctor who treats chest pain, high blood pressure, and heart failure, as well as issues with our heart valves, blood vessels, and other heart and vascular problems. To figure out what’s wrong, they can order tests like electrocardiograms, echocardiograms, and CT scans (computed tomography). With their diagnosis, they can prescribe medication, assist you in developing healthier exercise and eating habits, or perform cardiac catheterization.
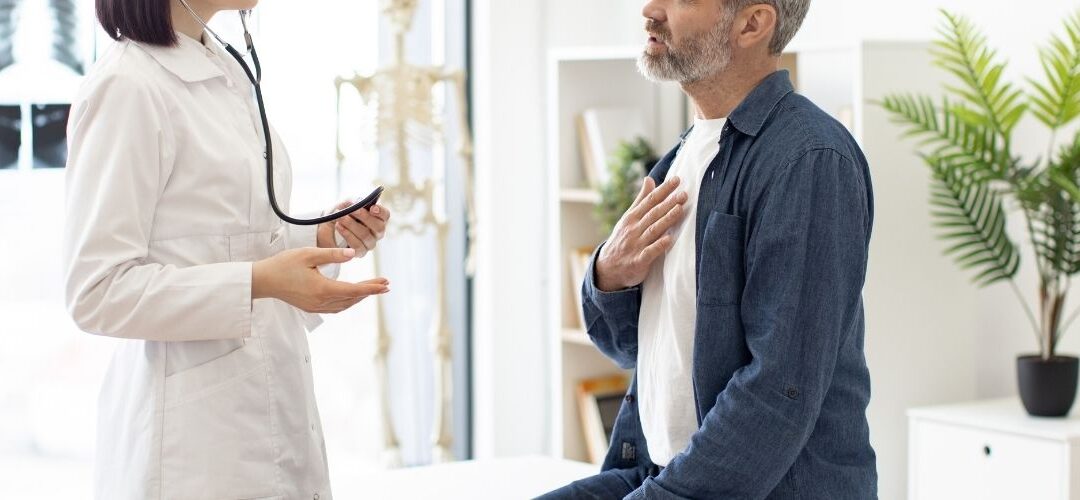
A cardiologist will examine us and discuss the symptoms, medical history, and family history. It is important to inform the cardiologist if other members of the family have had heart problems, as this can increase the chances of having a heart problem.
When would we require to visit a cardiologist?
A cardiologist can perform tests to determine whether patients have a heart murmur or an abnormal heart rhythm.
Patients who have had a heart attack, heart failure, or other heart problems are frequently treated. They assist in the decision-making process for heart surgery, heart catheterization, angioplasty, and stenting. If a patient exhibits signs of a heart condition, their doctor may refer them to a cardiologist.
Symptoms of a heart problem include:
- Breathing difficulty
- Dizziness.
- Chest discomfort
- Heart rhythm or beat changes.
- Elevated blood pressure
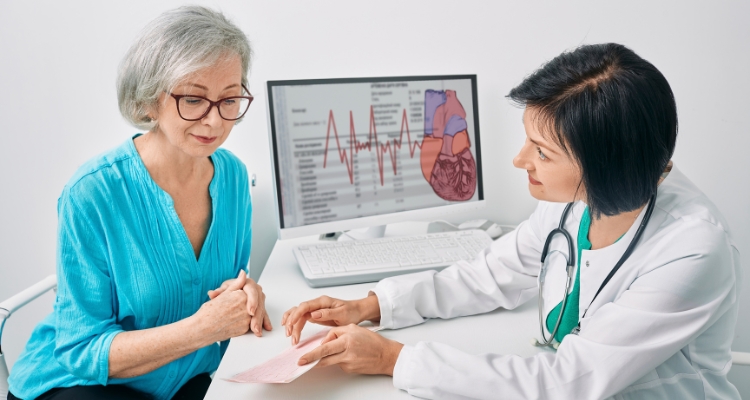
What to Expect at a Cardiology Consultation
A cardiologist will perform a physical exam, paying close attention to your heart. They can detect irregular heart rhythms and how well blood flows through our heart. We have to
Start preparing answers of questions about our family history as well as personal medical history. If the siblings, parents, or other family members have had heart problems, the cardiologist will want to know. Knowing this information can help the cardiologist determine what types of heart problems patients may be experiencing.
Choosing a Cardiology Specialist
Patients are frequently referred to a cardiologist by their primary care physician, but they may prefer to select their own specialist.
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends that patients confirm that their cardiologist is board certified. Patients can confirm this with the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) or the American Board of Family Medicine (ABFM) (ABFM).
It is also essential to choose a doctor whose style of communication is compatible with theirs.
If the cardiologist advises a treatment that appears risky or costly, or if the patient is unsure why they require this treatment, the AHA recommends to go look for other options.